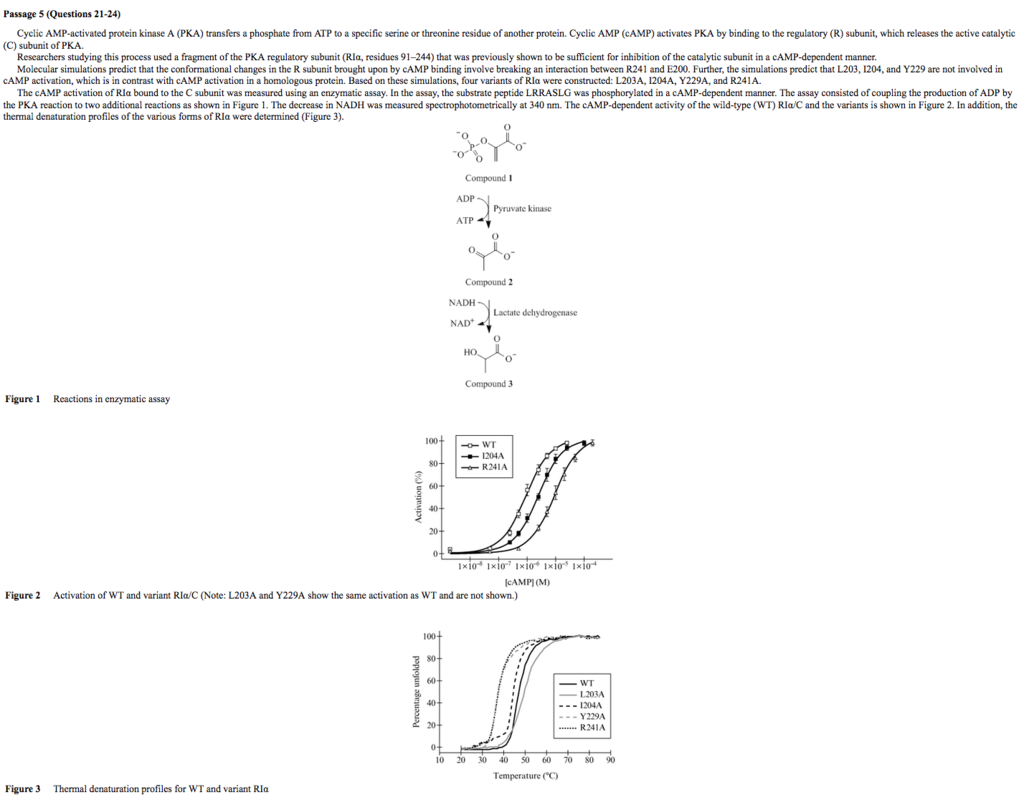
So Figures 2 and 3 are needed to answer the question. Figure 2 caption says the Y229A mutation shows the same activation as wild type, which means Y229A mutation doesn't affect cAMP activation. As such, Y229 is not critical for cAMP activation. Figure 3 shows a leftward curve shift for the Y229A thermal denaturation profile. This means more of the Y229A mutant protein is unfolded/denatured at lower temperature (look at the axes of Figure 3 chart). So Y229A mutation lowers the stability of the protein, which implies Y229 is necessary for protein stability.